Abstract
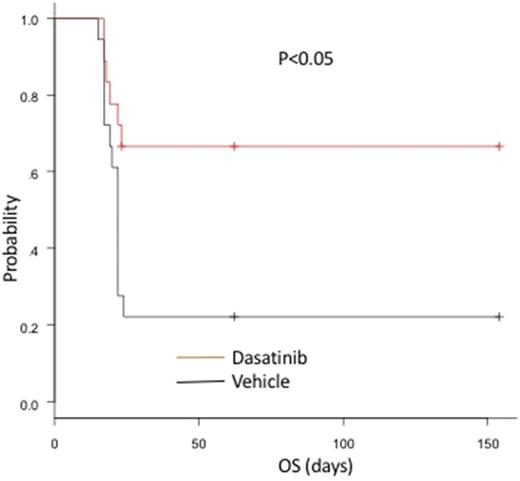
[Backgrounds] Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) belongs to nodal T-cell lymphoma with T follicular helper (TFH) phenotype. Both the G17V RHOA mutation and the loss-of-function TET2 mutation have been identified in 70% of AITLs. We previously demonstrated that G17V mutant RHOA augmented T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling though binding to VAV1, an essential component of the T-cell signaling pathway (Leukemia, in press). However, it remains elusive whether inhibition of TCR pathway serves as an effective treatment in AITL. [Methods] Activation of VAV1 and PLCgamma1 in response to TCR stimulation was examined in Jurkat cells inducibly expressing wild-type and G17V mutant RHOA under the treatment with dasatinib, a multi-kinase inhibitor. Nuclear factor of activated T cell (NFAT) activity was similarly examined in Jurkat cells transiently transfected with wild-type and G17V mutant RHOA. Mice expressing G17V RHOA under CD2 promoter (G17VRHOA mice) were crossed with MxCre Tet2f/f mice and pIpC was given to the offspring 4 weeks after birth to obtain Tet2-/- and Tet2-/-G17VRHOA mice. Whole transcriptome analysis was performed for CD4+ T cells purified from the spleen of tumor developed mice. Serum cytokines were examined by BD Cytometric Beads Assay. Cells derived from tumors developed in Tet2-/-G17VRHOA mice were transplanted into nude mice. Dasatinib was orally given at 5 mg/kg/day for 14 days. [Results] The G17V mutant RHOA enhanced phosphorylation of VAV1 and PLCgamma1, and NFAT reporter activity in Jurkat cells. The phosphorylation and the NFAT activity were efficiently blocked by dasatinib at 10 nM. Approximately 70% of Tet2-/-G17VRHOA mice died around 40 wo, while 14% of Tet2-/- and none of G17VRHOA mice died at the same age (p<0.05). All the moribund Tet2-/-G17VRHOA mice presented splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy. The lymph nodes and the spleens showed diffuse infiltration of tumor cells expressing TFH markers, i.e., CD4, PD1, and ICOS. The aberrant increase of high endothelial venules was observed in the swollen lymph nodes, mimicking human AITL. Whole transcriptome analysis followed by gene-set enrichment analysis revealed enrichment of Il-2/STAT5, Il-6/JAK-STAT3, and TNFα/NFκB signaling pathways in Tet2-/-G17VRHOA CD4+ spleen cells. The serum concentrations of Il-2, Il6, and TNFα in Tet2-/-G17VRHOA were significantly higher than control at the same age (p<0.05). The CD4+ cells in the enlarged spleen and the swollen lymph nodes in Tet2-/-G17VRHOA mice at 40 wo showed oligoclonal rearrangement of TCR genes. Nude mice transplanted with tumor-derived cells showed splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy preceded by elevation ofthe serum concentrations of Il-2, Il-6 and TNFα (before vs. after the transplantation, 4.33±0.14 vs. 4.80±0.37, 5.85±2.96 vs. 34.92±15.49, and 7.68±2.08 vs. 45.70±33.72, p<0.01, respectively). Mice given with dasatinib starting at 10 days after the transplantation showed higher overall survival compared to the vehicle control (p<0.05, Figure 1). The serum concentrations of Il-2, Il-6, and TNFα were decreased in dasatinib group (before vs. after the dasatinib treatment, 4.85±0.40 vs. 4.28±0.18, 38.23±18.74 vs. 10.01±7.38, and 48.37±34.6 vs. 18.67±12.37, p<0.05, respectively).
Discussions and Conclusion: The combination of G17V mutantRHOAexpression and Tet2 deletion led to development of AITL-like tumors in mice, which were hughly effectively treated by dasatinib. This model may also be useful to examine novel treatment strategies for AITL, other than dasatinib.
Chiba: Nippon Shinyaku: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal